The Next Great Leap: Pushing Intelligence to the Perimeter
Generative AI—the technology powering image creation, large language models (LLMs), and complex data synthesis—has historically relied on massive, centralized cloud servers. However, the future of AI is moving closer to the user. Edge Computing—processing data where it is created, whether on a smartphone, an autonomous vehicle, or an industrial sensor—is merging with Generative AI to create a new paradigm.
This convergence, termed Generative AI in Edge Computing, promises to revolutionize key industries by solving three critical bottlenecks of traditional cloud AI: latency, bandwidth, and data privacy. For professionals, developers, and security architects (35-55), understanding this shift is crucial for future deployment and infrastructure planning.
This deep dive explains how this technological fusion is enabling real-time interaction and personalized services while maintaining robust privacy, delivering the ultimate guide to Edge AI Integration for Generative Models.
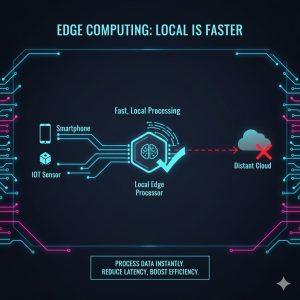
Pillar 1: The Core Technical Imperatives—Latency and Bandwidth
The most immediate drivers for moving Generative AI to the edge are practical physics: the speed of light and the cost of bandwidth.
Solving the Latency Problem
When a mobile device sends a prompt to a cloud LLM, the request and response can travel hundreds or thousands of miles. This round-trip distance (latency) creates an noticeable delay, severely limiting real-time applications like instant conversational AI or immediate image generation.
-
Edge Solution: By running pruned or compressed Generative Models (like smaller, quantized LLMs or diffusion models) directly on a device’s Neural Processing Unit (NPU), the processing time is reduced to milliseconds. This enables truly instantaneous interaction, which is vital for applications in robotics, autonomous systems, and advanced mobile assistance.
-
Example: Autonomous vehicles require instantaneous decision-making based on sensor data. Waiting for cloud confirmation is impossible. Edge AI allows the vehicle to locally process sensor data and generate immediate action plans.
-
Minimizing Bandwidth Dependence
Running massive models in the cloud generates enormous data traffic, leading to high operational costs and slow performance in areas with limited connectivity (e.g., remote factories, rural areas).
-
Edge Solution: Edge AI significantly cuts down on the amount of raw data that must be transmitted. Only summarized or critical output data is sent to the cloud, dramatically reducing bandwidth requirements and increasing overall system efficiency—a key component of Edge AI Integration for Generative Models.
Pillar 2: Privacy and Security Reinforcement
For many enterprises, sensitive data (medical records, proprietary designs, or personal communications) cannot legally or ethically leave the local device or secure network. This is where Generative AI in Edge Computing offers a critical security solution.
Local Data Processing
When the generative model runs locally, the raw input data—your voice recording, your corporate document, or your sensitive image input—never leaves the perimeter of the device or local server.
-
Privacy by Design: This architecture adheres to strict ‘Privacy by Design’ principles. The AI processes the data locally and only outputs the synthesized, non-identifiable result (e.g., a summarized text or a modified image) to the cloud, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
-
Federated Learning: This model allows multiple edge devices (e.g., thousands of smart cameras) to train a shared Generative AI model collaboratively. The model is updated based on local insights, but the raw data itself stays partitioned on the original devices, preserving user privacy while improving collective intelligence.
Enhanced Security
By reducing the dependency on a single, centralized cloud server, the system reduces the risk of massive data breaches that plague traditional cloud infrastructure. The attack surface is distributed across thousands of individual edge nodes.

Pillar 3: Use Cases and Mobile Interaction Revolution
The shift to Generative AI in Edge Computing is creating a new category of intelligent, personalized applications, transforming both the industrial and consumer landscapes.
Transforming Industrial IoT
Industrial applications require high reliability and low latency, making them ideal for edge deployment.
-
Predictive Maintenance: AI models running on factory edge servers can analyze real-time sensor data from machinery and generate predictive failure models (Digital Twins) instantly, stopping potential downtime before it occurs.
-
Quality Control: High-speed vision systems on a manufacturing line use edge AI to instantly identify and flag defects, generating reports locally without delay.
The Mobile Experience Revolution
For the consumer, edge AI is making mobile interaction more fluid and personal than ever before.
-
On-Device LLMs: Modern flagship smartphones can now run smaller LLMs locally. This enables instant text summarization, immediate translation, and complex task automation directly on the phone, freeing users from reliance on Wi-Fi or cellular connectivity.
-
Personalized Media: Generative AI can personalize video or audio feeds in real-time based on local user context, creating a hyper-relevant mobile interaction experience.
This integration is defining the future of ubiquitous, responsive, and private smart technology. Edge AI Integration for Generative Models is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity.

REALUSESCORE.COM Analysis Scores: Edge AI Integration for Generative Models
This analysis evaluates the current readiness and transformative potential of integrating Generative AI into Edge Computing infrastructure.
| Analysis Feature | Current Readiness (1-10) | Transformative Impact (1-10) | Analysis Explanation |
| Latency Reduction | 8.5 | 9.8 | Solves the critical real-time bottleneck for instantaneous mobile/autonomous interaction. |
| Data Privacy & Security | 9.0 | 9.5 | Enables processing of highly sensitive data locally, complying with strict privacy mandates. |
| Model Optimization (Compression/Pruning) | 8.0 | 8.5 | Requires ongoing development to shrink large models without significant performance degradation. |
| Bandwidth & Cost Saving | 9.2 | 9.0 | Dramatically reduces data transmission volumes and cloud processing costs for enterprises. |
| Hardware Dependency (NPU) | 7.5 | 8.5 | Requires specialized, efficient Neural Processing Units (NPUs) in edge hardware, limiting legacy adoption. |
| Overall Future Value | 8.4 | 9.3 | Generative AI in Edge Computing is the definitive architecture for the next decade of AI deployment. |
Conclusion: The Edge is the Future of Generative AI
The move of Generative AI from the centralized cloud to the distributed edge is not merely an optimization—it is a foundational architectural shift. By effectively solving the problems of latency, bandwidth, and data sovereignty, Generative AI in Edge Computing is unlocking mission-critical applications in autonomous systems and securing user data in consumer devices.
For developers and enterprises, prioritizing Edge AI Integration for Generative Models is essential. The future of intelligent, instantaneous, and private mobile interaction is no longer in the cloud; it is at the perimeter.

