The Evolution of AI: From Tools to Teammates
The biggest shift in the AI landscape is the move from simple Large Language Models (LLMs) that respond to prompts, to complex Autonomous Digital Workers—AI agents capable of planning, executing multi-step tasks, and communicating with other agents and external APIs. These workers are poised to automate entire business processes, from code generation and debugging to market research and dynamic enterprise planning.
For developers, solution architects, and technical leaders (35-55), choosing the right AI Agent Development Platform is the difference between scalable automation and a frustrating Proof-of-Concept. The three dominant contenders are the veteran LangChain vs AutoGen vs Google’s Framework (referring to Google’s specialized agent development tools like the Gemini API and integrated platforms).
This Developer Guide provides an essential architectural comparison, breaking down the strengths of each platform for building robust, self-directing AI systems for the enterprise in 2025.

Pillar 1: Architecture and Ecosystem—Foundation for Autonomy
The structural foundation of these platforms dictates their flexibility, integration capability, and complexity.
LangChain: The Modular Veteran
LangChain is the oldest and most widely adopted framework. It is an open-source, modular toolbox designed to chain together LLMs, external data sources, and computational steps.
-
Core Strength: Modularity. LangChain uses concepts like Chains (sequences of calls), Agents (decision-making loops), and Tools (APIs or functions) that can be swapped out easily. It’s highly LLM-agnostic, supporting virtually every major model (OpenAI, Gemini, Mistral, etc.).
-
Developer Focus: Ideal for developers who need maximum customization and wish to build highly bespoke, single-agent workflows (RAG systems, simple decision loops).
AutoGen: Built for Conversation
Developed by Microsoft, AutoGen is explicitly designed for building Multi-Agent Systems. It abstracts away much of the boilerplate code required for agent communication.
-
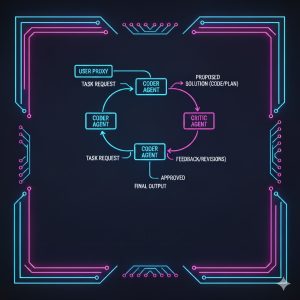
Core Strength: Inter-Agent Communication. AutoGen allows developers to define a group of agents (e.g., a Coder, a Critic, an Executor) that automatically converse and debate using natural language until a task is completed. This makes building complex, collaborative Autonomous Digital Workers significantly faster.
-
Developer Focus: Best for projects that require collaborative problem-solving, code review, or dynamic team workflows.
Google’s Framework: Integrated Power
Google’s approach, primarily through its Gemini API and specialized AI Agent Builder interfaces, emphasizes deep integration with its cloud infrastructure (Google Cloud) and powerful foundation models (Gemini).
-
Core Strength: Enterprise Integration and Tooling. The framework is optimized for running Gemini’s native functions, offering superior performance for tasks involving Google Search (Grounding), Workspace APIs, and Google Cloud services. This provides native reliability for large enterprise deployments.
-
Developer Focus: Preferred by enterprises deeply invested in the Google ecosystem seeking maximum performance and security from their AI Agent Development Platform.
Pillar 2: Agent Communication and Collaborative Problem-Solving
The ability for agents to communicate and self-correct is the hallmark of true autonomy.
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
| Platform | Communication Style | Best Use Case |
| AutoGen | Conversational, Free-Form | Code generation/review, Collaborative planning, Data analysis |
| LangChain | Structured, Sequential | Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), Defined tool usage flows |
| Google’s Framework | API/Function-based, Grounded | Data synthesis, Fact-checking, Integration with enterprise tools |
AutoGen excels here by making the agent “team meeting” a first-class citizen. Its core loops are designed around agents sending messages and awaiting consensus or critique before proceeding. This drastically reduces the complexity of programming iterative refinement.
While LangChain can achieve Multi-Agent Systems, it requires more custom coding of the underlying communication logic, often relying on sequential task routing rather than open-ended dialogue.
Pillar 3: Deployment, Enterprise Readiness, and Future-Proofing
For industrial application, an AI Agent Development Platform must be secure, scalable, and easy to maintain.
Enterprise Readiness
-
Google’s Framework: Its strong tie to Google Cloud naturally gives it a head start in terms of enterprise-grade security, logging, and scalability features (like Vertex AI deployment). The built-in compliance and governance tools are a major advantage for large organizations.
-
LangChain: As an open-source tool, its deployment model is highly flexible but requires more management overhead (self-hosting, security patching, and scaling infrastructure). However, its LLM-agnostic nature provides exceptional vendor diversity protection.
-
AutoGen: Also open-source, it shares LangChain’s deployment flexibility but currently has a smaller, less diverse ecosystem of third-party enterprise tools, though this is rapidly growing.
Data Grounding and Tool Use
All three platforms are proficient in RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation). Google’s native access to powerful “Grounding” tools (like Google Search and Google Knowledge Graph) is a built-in advantage, providing highly reliable, factual results directly to its Autonomous Digital Workers. LangChain and AutoGen rely on integrating third-party search APIs or custom RAG vectors.
The future-proofing of these platforms is tied to the evolution of the LLMs they support. LangChain’s modularity makes it the safest bet against vendor lock-in, but Google’s continuous investment in its proprietary models and frameworks guarantees bleeding-edge performance.

REALUSESCORE.COM Analysis Scores: Digital Worker Frameworks
| Analysis Feature | LangChain | AutoGen | Google’s Framework | Analysis Explanation |
| Multi-Agent Communication Ease | 7.0 | 9.8 | 8.5 | AutoGen is explicitly designed for seamless, conversational agent collaboration. |
| LLM Agnostic Flexibility | 9.9 | 9.0 | 7.5 | LangChain’s modular structure offers the least vendor lock-in. |
| Enterprise Scalability/Security | 8.0 | 8.0 | 9.5 | Google’s deep integration with GCP provides superior native governance and scaling. |
| Tool/API Integration Depth | 9.0 | 8.5 | 9.2 | All are strong; Google offers native grounding and Workspace integration. |
| Community and Documentation | 9.5 | 9.0 | 8.5 | LangChain has the largest community base due to its head start and open-source nature. |
| Overall Autonomous Worker Value | 8.7 | 9.1 | 8.8 | AutoGen offers the best framework for building collaborative Autonomous Digital Workers today. |
Conclusion: Which AI Agent Development Platform Wins?
If your priority is enterprise deployment, security, and integration with existing business tools, Google’s Framework offers the most seamless and robust solution.
If your core requirement is maximum flexibility and LLM diversity, LangChain remains the indispensable modular Swiss Army knife for building bespoke agent applications.
However, for developers focused on the next evolution—creating teams of Autonomous Digital Workers that collaborate, debate, and solve problems with minimal oversight—AutoGen is the definitive winner of the LangChain vs AutoGen vs Google’s Framework showdown, offering the most elegant and efficient AI Agent Development Platform architecture available today.