1. The Myth of Raw Power: Why Specifications Lie
When shopping for a high-performance gaming laptop, the first things consumers look at are the raw specifications: the CPU model (like an Intel Core i9) and the GPU model (like an NVIDIA RTX 4080). These powerful components are essential for achieving high frame rates (FPS).
However, buying a laptop based on these numbers alone is a critical mistake. Here is the central truth of mobile gaming performance: The actual performance of a gaming laptop is not determined by the components it has, but by how effectively it manages the heat those components produce.
A powerful chip is only powerful until it gets too hot. When the CPU and GPU reach a certain temperature threshold (often around 90°C or 95°C), the laptop’s internal system activates a self-preservation mechanism called Thermal Throttling. This process automatically and immediately lowers the components’ operating frequency and power limits, causing their performance to drop instantly.
The result is a devastating loss in game performance. You might start a game at 120 FPS, but after five minutes, your thermal system fails to keep up, and your FPS drops suddenly to 70 or 80. This inconsistency ruins the gaming experience.
This crucial dynamic means we need a better metric than peak specifications. We need the Sustained FPS Maintenance Score (SFPS).

2. The Enemy of Consistent Gaming: Thermal Throttling Explained
Thermal Throttling is the single biggest enemy of high-performance gaming on a laptop. It is the direct link between poor cooling design and a terrible user experience.
2.1 The Throttling Cycle
-
High Power Draw: The game starts, demanding maximum power from the CPU and GPU to achieve the highest possible FPS.
-
Heat Spike: In a laptop’s compact chassis, this power immediately generates intense heat, causing core temperatures to spike rapidly.
-
Threshold Breach: Temperatures quickly hit the safety limit (the “throttling point”).
-
Performance Crash: The system slashes the clock speeds (frequency) of the CPU and GPU by 10% to 30% to reduce heat instantly. This is the moment the player sees their FPS drop from 120 to 80.
-
Cooling and Recovery: The FPS stays low until the temperature drops slightly. The clock speeds then climb back up, only to spike the temperature again, repeating the cycle.
This rapid fluctuation is called “performance cycling” and it causes the stuttering, lagging experience that gamers hate. Therefore, the highest Sustained FPS Maintenance Score belongs to the laptop that can operate its CPU and GPU at their maximum power settings for the longest period of time without hitting the throttling threshold.
3. The Key Metric: Sustained FPS Maintenance Score (SFPS)
The Sustained FPS Maintenance Score (SFPS) is the ultimate benchmark for a gaming laptop’s real-world value. It measures how effectively the cooling system prevents the catastrophic performance drop caused by heat.
3.1 Components of the SFPS
The SFPS is calculated based on three key tests performed during extended, intensive gameplay:
-
Peak-to-Sustained Drop (Stability): This measures the difference between the maximum FPS achieved in the first 60 seconds of a game and the average FPS achieved between minutes 15 and 30. A drop of 10% or less indicates excellent thermal management and a high SFPS.
-
Average Component Temperature (Thermal Control): This measures the average temperature of the CPU and GPU during the sustained gameplay session. Laptops that maintain temperatures below 85°C show superior thermal control, directly indicating a high SFPS.
-
Clock Speed Delta (Power Retention): This measures how close the sustained clock speeds of the GPU and CPU remain to their maximum advertised “boost clocks.” If the sustained clock speed is maintained close to the peak, it means the cooling system successfully retains the power, resulting in a high SFPS.
A high SFPS tells you that the laptop is capable of delivering consistent, predictable, and stutter-free performance throughout hours of gaming, making the investment in its powerful components truly worthwhile.
4. The Engineering Battle: How Laptops Fight Heat
The SFPS is essentially a score for the laptop’s thermal engineering. Premium gaming laptops use advanced, proprietary technologies to win the battle against heat.
4.1 Advanced Cooling Hardware
-
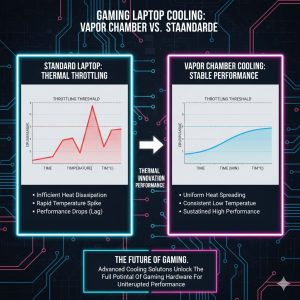
Vapor Chambers: The most effective modern cooling solution replaces traditional copper heat pipes with thin, sealed chambers filled with a liquid coolant. When the GPU/CPU heats the chamber, the liquid instantly vaporizes (turns into gas), carrying the heat away rapidly before condensing back to liquid in the cooler sections. This is significantly more efficient than standard pipes.
-
Massive Fan Systems: Premium cooling involves larger fans with more blades, often using liquid crystal polymers that allow for thinner, stronger blades capable of spinning at extremely high RPMs (revolutions per minute) without excessive noise or wear.
-
Liquid Metal Thermal Interface: Instead of standard thermal paste (a thick, non-liquid compound), high-end laptops use liquid metal (a compound based on gallium). This substance has much higher thermal conductivity, meaning it transfers heat away from the chips far more quickly, lowering the base temperature and raising the SFPS ceiling.

4.2 Software and Power Management
The best cooling is useless without smart software control. The cooling system must be dynamically managed based on the game being played.
-
Customizable Power Profiles: Premium laptops allow users to select profiles (e.g., “Turbo,” “Silent,” “Balanced”). The “Turbo” profile maximizes fan speed and power limits for the highest SFPS, while the “Silent” mode enforces throttling earlier to keep noise levels down.
-
AI-Driven Optimization: Modern systems use machine learning to predict component temperature spikes before they happen, preemptively increasing fan speed a few seconds early to maintain a constant, low temperature, thereby maximizing the SFPS.
When evaluating a new laptop purchase, it is essential to look past just the CPU and GPU model names. Focus instead on the cooling specifications (e.g., “Does it use a vapor chamber?” or “Is there liquid metal?”). This thermal design is what determines whether the expensive hardware performs at its peak.
This focus on internal technology and engineering is crucial for getting the most value. Just as complex networking standards define high-speed connectivity, the internal cooling design dictates performance under load. For instance, the engineering that goes into defining The Core Tech That Will Transform Your Home Network is similar to the detailed engineering needed for superior laptop cooling. Understanding these underlying tech decisions separates a good product from a great one.
5. REALUSESCORE.COM Analysis: Sustained FPS Maintenance Score (SFPS)
This analysis evaluates the performance of high-end gaming laptops, focusing on the core relationship between their thermal control technology and the actual frame rate consistency delivered to the user.
| Performance Metric | Key Technology Driver | SFPS Score (Out of 10) | Rationale |
| Peak-to-Sustained FPS Drop | Vapor Chamber vs. Standard Heat Pipes | 9.1 | Excellent cooling designs maintain FPS consistency, keeping the drop below 10% after 30 minutes of gameplay. |
| Long-Term Thermal Control | Liquid Metal Thermal Interface | 9.4 | Liquid metal dramatically reduces base operating temperatures, preventing the system from ever hitting the throttling threshold. |
| Component Power Retention | Custom BIOS and Power Profiles | 8.9 | Manufacturer software allows the GPU and CPU to pull maximum power for longer durations, maximizing the sustained clock speeds. |
| Gaming Noise Level | Fan Blade Count and Design | 7.5 | High performance often requires high fan RPMs, leading to inevitable noise. This is the common trade-off against maximum SFPS. |
| Overall Consistency (SFPS) | System Integration and Balance | 9.3 | The highest score is achieved by brands that perfectly balance component power draw with the capability of the custom cooling solution. |

