The Evolution of Code Review: From Manual Audits to AI-Driven Development
The 2026 software development landscape is defined by the triple challenge of speed, complexity, and rigorous security demands. Large Language Model (LLM)-powered AI coding tools are no longer confined to simple code completion. They have penetrated deep into the core of the development pipeline—specifically in Code Review and Security—fundamentally reshaping enterprise IT budgets and developer productivity.
This comprehensive analysis moves beyond the basic function of “code generation” to provide an in-depth evaluation of two market leaders: GitHub Copilot and Tabnine. We assess which solution is better suited for large-scale organizations, focusing on critical enterprise metrics: Code Quality, Security Governance, and Enterprise Integration (TCO).
1. Code Generation Models and Performance: Accuracy vs. Customization
The fundamental distinction between these tools lies in their training data philosophy and how they approach code suggestion, directly impacting enterprise adoption.
1.1 GitHub Copilot: Large-Scale Public Data Model and Contextual Completion
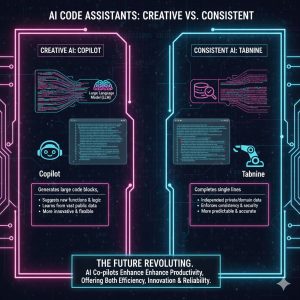
GitHub Copilot, powered by the OpenAI Codex model, is trained on a massive corpus of public code. This model excels at highly creative, contextual suggestions, often generating entire functions or classes based on a few natural language prompts or existing code context.
-
Performance Strength: Copilot’s strong contextual awareness allows it to suggest dozens of lines of complex logic instantly. This capability maximizes development velocity, especially for generic, well-documented patterns, accelerating the initial drafting of features.
-
Enterprise Challenge: Relying on public data means the generated code may not adhere to the organization’s proprietary coding standards or legacy architectures. Additionally, the developer inherits the risk of integrating potential security vulnerabilities or uncertain open-source licensing derived from the vast public training set.
1.2 Tabnine: Private Code Base Training and Predictability
Tabnine sets itself apart by specializing in creating custom models trained directly on a customer’s private repositories (Private Code Base). This focus is exceptionally powerful for organizations that need the AI to deeply understand and enforce their unique domain knowledge, internal API usage, and corporate code style.
-
Performance Strength: Tabnine’s suggestions exhibit superior consistency with the company’s existing codebase. This significantly reduces time spent on style validation during the code review process and speeds up the time-to-productivity for new developers joining the team.
-
Enterprise Challenge: Tabnine’s creativity may be more limited compared to Copilot, particularly when generating entirely novel, long code blocks. Its performance is highly dependent on the quality and volume of the internal training data, and the initial model build-out process requires a significant time investment. For a deeper dive into maintaining stability: MLOps and Deployment: Ensuring Stable AI in Production Environments and Avoiding Drift
| Feature Comparison | GitHub Copilot | Tabnine |
| Foundation Model | OpenAI Codex (Public Code Focus) | Proprietary Models (Private Code Training) |
| Code Generation Scope | Long functions, classes, complex logic (High Creativity) | Line completion, variable/function signature (High Consistency) |
| Enterprise Customization | Limited | Extremely Strong (Key Differentiator) |
| Primary Enterprise Benefit | Accelerated development velocity, initial feature drafting | Code quality consistency, improved developer onboarding speed |
2. Enterprise Security and Governance: Data Sovereignty and Risk Mitigation
For organizations in regulated sectors, security and data isolation are critical deal-breakers for AI adoption.
2.1 Data Isolation and Privacy
The paramount concern for enterprises is preventing the leakage of proprietary code or its unintended use for training external AI models.
-
GitHub Copilot (Enterprise): While Microsoft guarantees that customer code is not used for external model training in its Enterprise tiers, the service is fundamentally cloud-hosted. This necessitates thorough vetting of data flow and clear boundary setting.
-
Tabnine (Enterprise): Tabnine offers Air-Gapped or On-Premise deployment options. This allows the custom models to be trained and deployed entirely within the customer’s private network, ensuring zero exposure to external cloud services. This capability provides a non-negotiable advantage in industries (e.g., Finance, Defense, Healthcare) requiring strict data sovereignty and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
2.2 Managing Vulnerability and License Risk
AI-generated code inherently carries the risk of introducing latent security flaws or infringing on open-source licenses.
-
GitHub Copilot: Copilot provides some integrated security checks. However, due to its reliance on vast public data, the risk of incorporating code with problematic licenses (Attribution) or known vulnerabilities remains, placing the ultimate burden of risk assessment on the human reviewer.
-
Tabnine: Because Tabnine trains on internal code, license attribution issues are significantly mitigated. More critically, Tabnine can be trained to recognize and flag patterns that violate internal security policies, enabling pre-detection and reduction of security flaws before they ever reach the formal code review stage.
![]()
3. Integration Ecosystem and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
A tool’s enterprise suitability is determined by its seamless integration into the existing development toolchain and its overall cost structure.
3.1 IDE and CI/CD Pipeline Integration
-
IDE Support: Both Copilot and Tabnine offer excellent, comprehensive support across all major Integrated Development Environments (IDEs), including VS Code, IntelliJ, and PyCharm.
-
CI/CD Linkage: Tabnine’s customized nature demands tight integration with the company’s Version Control Systems (VCS) and CI/CD pipelines (e.g., GitLab, Bitbucket). This constant synchronization allows for continuous model learning and update cycles, ensuring the AI is always current. While this increases initial setup complexity, it guarantees model freshness. Copilot integrates as a simpler, more independent service layer.
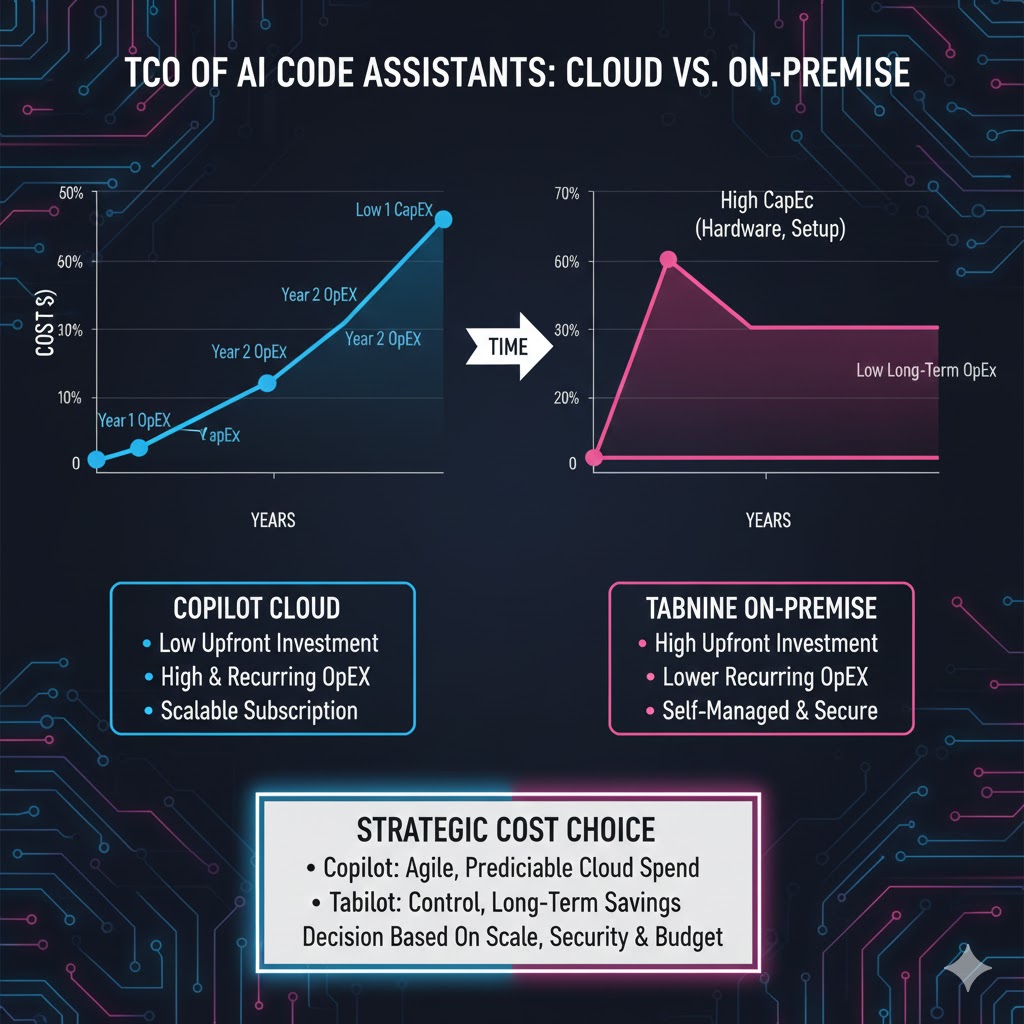
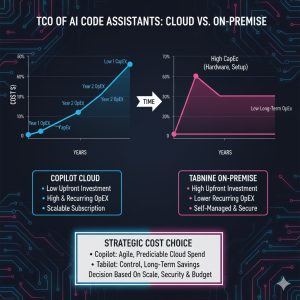
3.2 TCO Analysis: Operational vs. Strategic Investment
-
Copilot (OpEx Model): Copilot is typically purchased as a simple, predictable per-seat, per-month operational expenditure (OpEx) subscription. This model features low initial deployment costs but requires a higher hidden operational cost related to compliance auditing and manual code vetting.
-
Tabnine (Strategic CapEx/OpEx Hybrid): Tabnine’s on-premise model requires an initial Capital Expenditure (CapEx) for infrastructure and setup to host the custom models. However, this is balanced by significant long-term OpEx savings derived from faster, higher-quality code generation, reduced security compliance risk, and accelerated developer onboarding. For organizations with hundreds of developers, Tabnine’s controlled and customizable approach often delivers a superior long-term Return on Investment (ROI).
4. Final Verdict: Strategic Choice for Enterprise
The choice between GitHub Copilot and Tabnine boils down to a fundamental trade-off between Speed and Novelty (Copilot) versus Security and Consistency (Tabnine).
For highly regulated industries or organizations managing immense, proprietary, and complex codebases, Tabnine emerges as the superior strategic choice due to its capability for absolute data sovereignty, on-premise deployment, and powerful adherence to internal code standards.
For organizations that prioritize maximum velocity in feature development, operate primarily with modern, open-source stacks, and have a lower regulatory burden, GitHub Copilot provides an excellent, low-friction, high-velocity solution.
REALUSESCORE.COM Analysis Scores
| Evaluation Metric | GitHub Copilot | Tabnine | Rationale for Enterprise |
| Code Generation Speed | 9.5 | 8.0 | Copilot’s public model enables fast, broad, and creative code drafting. |
| Code Consistency/Quality | 7.5 | 9.6 | Tabnine excels by learning and enforcing the enterprise’s private, proprietary code standards. |
| Data Security & Isolation | 8.5 (Cloud-based Enterprise) | 10.0 (Air-Gapped Option) | Tabnine’s on-premise offering is non-negotiable for strict data sovereignty requirements. |
| Integration Complexity (Lower is Better) | 9.0 | 7.5 | Copilot is simpler to deploy; Tabnine requires complex, high-value CI/CD integration for custom learning. |
| Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) | 8.5 (Lower Initial Cost) | 9.0 (Higher ROI through security compliance and code quality) | Reduced audit time and minimized breach risk make Tabnine financially stronger long-term. |
| REALUSESCORE.COM FINAL SCORE | 8.7 / 10 | 9.2 / 10 | Tabnine provides the essential security and control features required for large, risk-averse enterprises. |